Cholecystectomy Simulation Model
Awarded the Vesalian Scholar Award
Abstract
Cholecystectomies are one of the most common surgeries performed. Most complications that arise are from a bile duct injury. This causes a secondary procedure that is more invasive. It leads to increased costs and longer recovery time. To help prevent complications, surgical simulations are used to improve the skills within the operating room.
The intended goal for this project was to produce a low cost anatomically correct surgical model that not only mimics living tissue dynamics, but also provides similar electrical conductivity as human tissue.
The audience for this project is surgical residents and faculty within the Gastrointestinal Department and the Department of Surgery in the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University.
Model Overview
Digital Process
Horos - Dicom data from CT Scan
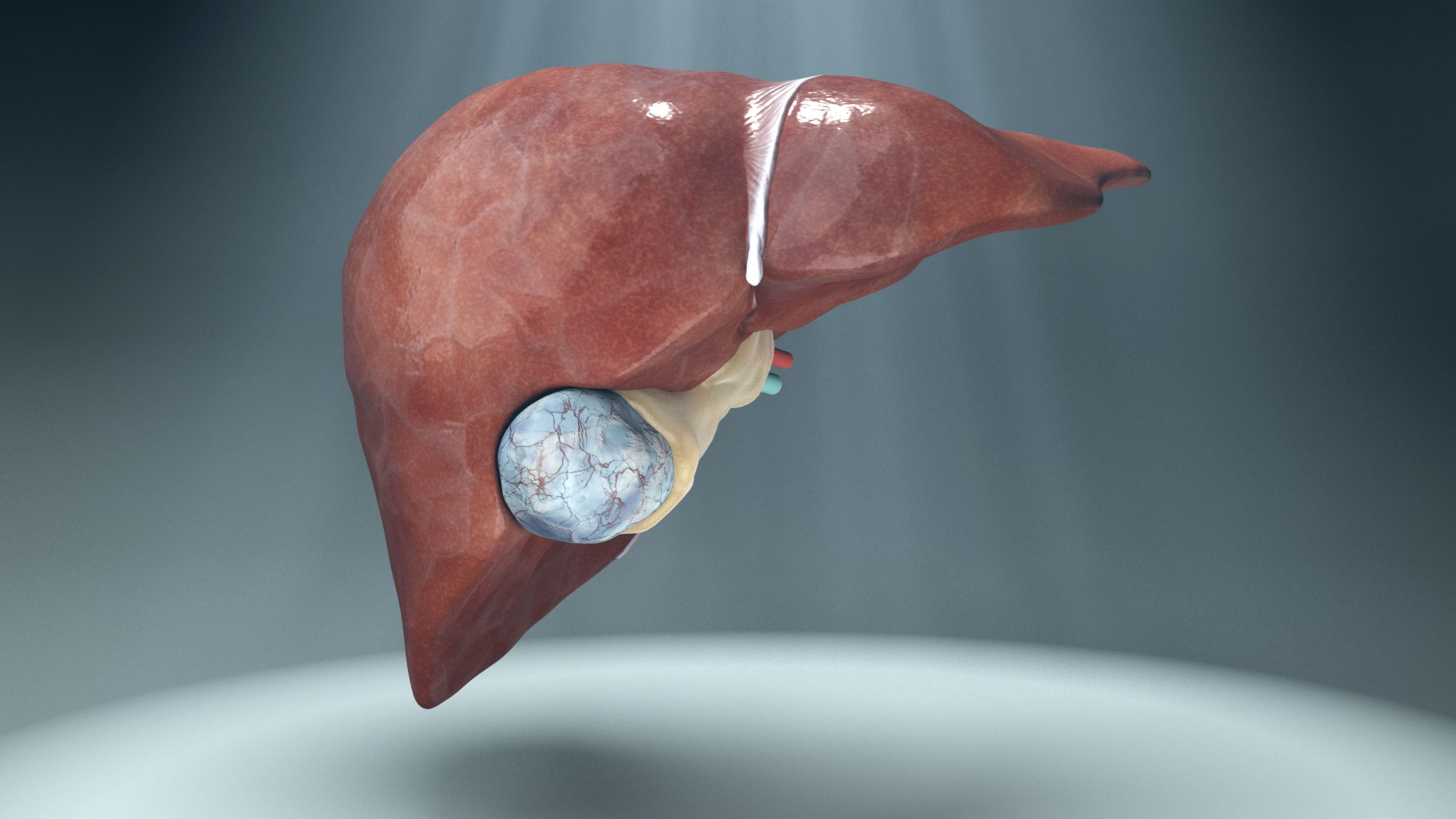
Zbrush - Remodeled the liver and gallbladder
C4D - Created the molds for liver, gallbladder, and vessels
Physical Process
3D Printer - Printed vessels and molds
Mold Casting - Created the final product using silicone.
Animation
Painted in Substance Painter
Rendered by Redshift in C4D
Animation of the Digital Process
Taken from dicom data
Remodeled
Physical Model
Model rendered in C4D by redshift
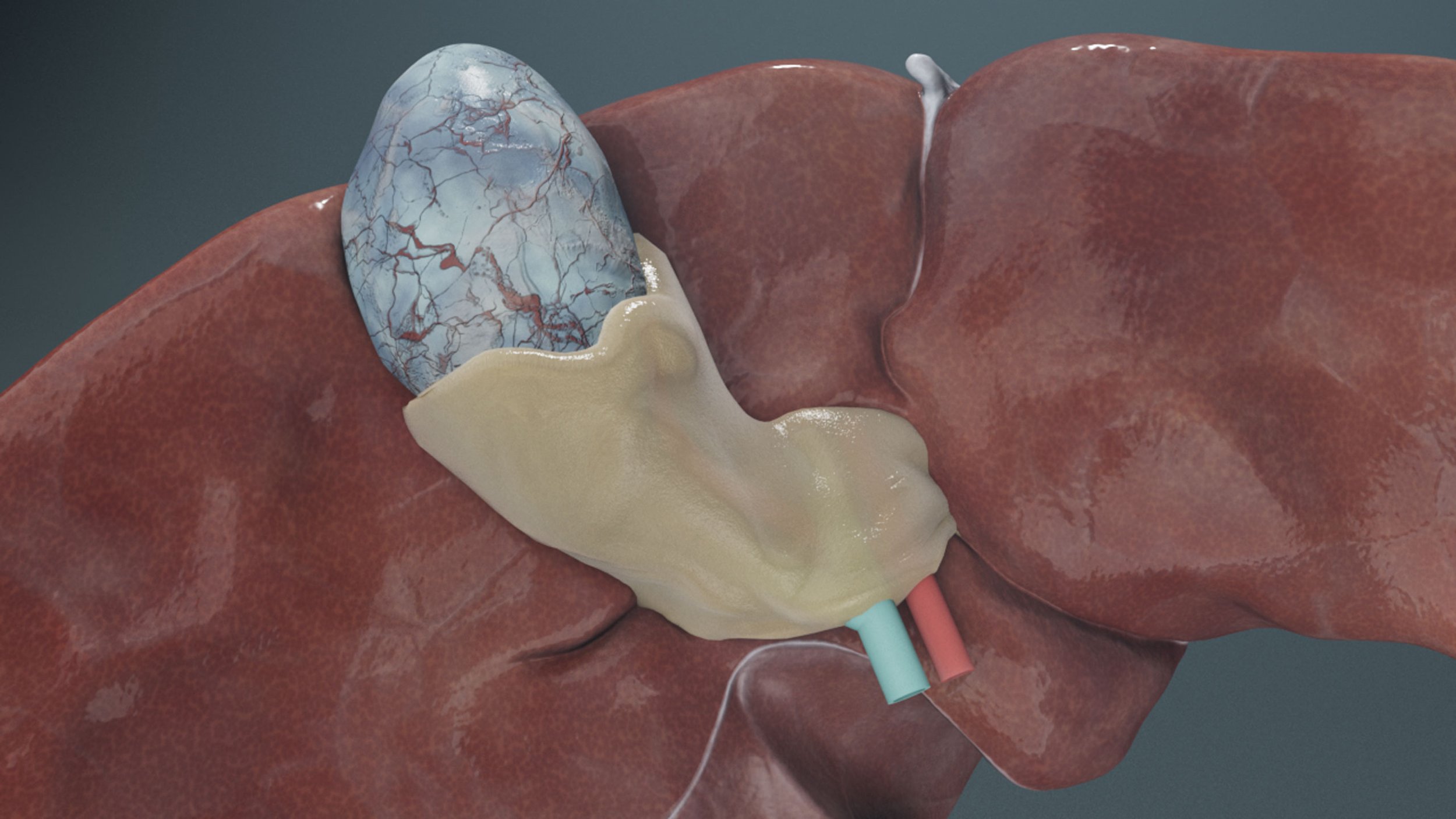
Anatomy of the Liver Model
Interactive Liver Model
Synthetic Adipose Tissue
The material is able to mimic living tissue dynamics as well as provide similar electrical conductivity as human tissue.
This material is self healing and can be reused.
Simulation Set Up
This model takes less than two minutes to prepare and can be reused immediately.
Place the first layer of synthetic adipose on the liver model.
Connect the gallbladder to the liver. The magnets will help it snap into place.
Attach the vessels to the model. The magnets will help them snap into place.
Place the second layer of synthetic adipose on the model.
Place the model in the simulation trainer.
The model is ready to be used.
This video demonstrates the steps to set up the model.
Final Simulation Model
Below are images taken from the simulation survey.
Survey Results
After conducting a survey of medical residents as well as surgeons, the results showed that the simulation is highly beneficial to medical training.